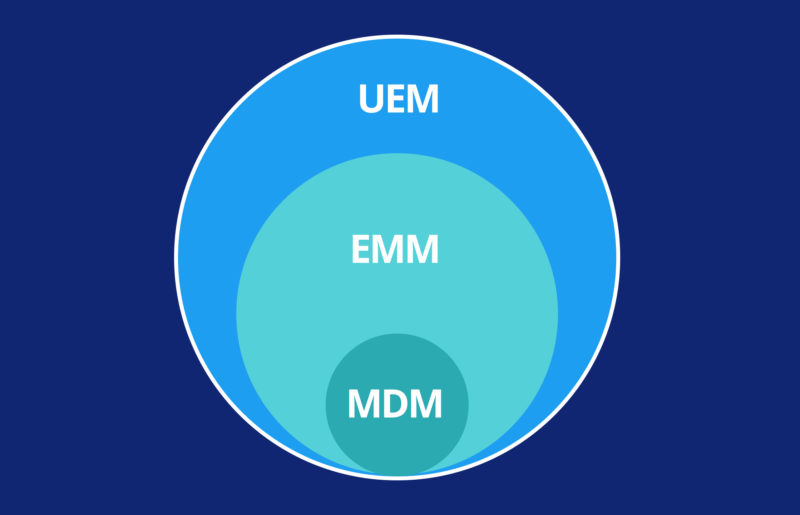
As the mobile workforce grows and remote work becomes the norm, businesses need effective solutions to ensure security, productivity, and seamless device management. This brings us to the pivotal debate between three core paradigms: Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM), Mobile Device Management (MDM), and Unified Endpoint Management (UEM). Twelve essential points of comparison among these approaches shed light on their unique strengths, weaknesses, and impact on your organisation’s mobile device management strategy.
Point 1: Scope and Definition
- EMM (Enterprise Mobility Management): EMM is a comprehensive approach that encompasses the management of mobile devices, applications, and content within an organisation. It extends beyond traditional MDM by incorporating mobile application management (MAM) and content management (MCM).
- MDM (Mobile Device Management): MDM focuses primarily on managing mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. It involves installing agents on these devices to enforce security policies, control access, and monitor device health.
- UEM (Unified Endpoint Management): UEM takes a holistic approach by managing many endpoints, including desktops, laptops, smartphones, tablets, and even IoT devices, all from a single unified platform. It integrates MDM, MAM, and MCM capabilities.
Point 2: Device Diversity
- EMM: EMM is adept at managing diverse device types and operating systems. It provides comprehensive support for various platforms, ensuring that all endpoints, regardless of type or OS, are effectively managed.
- MDM: MDM solutions are typically tailored for specific device types and OS, which lead to fragmentation and complexities as organisations adopt a wider range of devices.
- UEM: UEM excels in managing diverse devices. It offers robust support for multiple platforms and OS, providing a unified approach to managing various endpoints from a single interface. This simplifies device management in a heterogeneous environment.
Point 3: Security Management
- EMM: EMM strongly emphasises security management. It incorporates modern threat detection mechanisms, encryption, and secure access controls and integrates with threat intelligence feeds to provide real-time threat analysis and rapid incident response.
- MDM: MDM solutions offer core security features, such as antivirus and firewall management. However, they may lack advanced threat detection and response capabilities, leaving organisations vulnerable to evolving cyber threats.
- UEM: UEM solutions provide robust security features, combining the best of EMM and MDM. To ensure comprehensive security, they offer advanced threat detection, encryption, secure access, and threat intelligence integration.
Point 4: User Experience
- EMM: EMM solutions prioritise a seamless user experience. They offer features like over-the-air (OTA) updates, remote troubleshooting, and self-service portals. These capabilities minimise disruptions, ensuring that employees remain productive.
- MDM: MDM solutions, being device-centric, may sometimes disrupt user workflows. Applying updates or security patches can lead to downtime or interruptions.
- UEM: UEM solutions, like EMM, prioritise a seamless user experience. They provide OTA updates, remote troubleshooting, and self-service portals to minimise disruptions, enhancing security and user satisfaction.
Point 5: App Management
- EMM: EMM excels in app management. It offers robust app deployment, distribution, and updates across various devices and platforms. EMM solutions often include app containerisation to enhance security and compliance.
- MDM: MDM solutions primarily focus on managing desktop applications. They may lack features like app containerisation and advanced mobile app management.
- UEM: UEM offers comprehensive app management capabilities, including app deployment, distribution, updates, and containerisation. It bridges the gap between EMM and MDM by providing a unified approach to app management.
Point 6: Compliance and Reporting
- EMM: EMM solutions excel in compliance and reporting. They enforce policy compliance, track device adherence to security standards, and generate detailed reports. This is crucial for organisations in regulated industries.
- MDM: MDM solutions offer basic compliance monitoring but may lack extensive reporting capabilities, posing challenges in demonstrating compliance to auditors or regulatory authorities.
- UEM: UEM solutions provide comprehensive compliance monitoring and reporting features. They simplify audits and ensure that organisations meet regulatory requirements effectively.
Point 7: Remote Management
- EMM: EMM solutions are designed for effective remote management. They enable IT teams to troubleshoot and resolve issues remotely, configure devices, and provide user support efficiently.
- MDM: MDM solutions offer remote device management capabilities but may lack advanced remote support features.
- UEM: UEM solutions, like EMM, prioritise effective remote management. They facilitate efficient communication between IT teams and end-users, leading to smoother device management and improved productivity.
Point 8: Integration and Ecosystem
- EMM: EMM solutions are known for their integration capabilities. They often provide APIs and connectors for seamless integration with various enterprise systems, enhancing interoperability across the organisation.
- MDM: MDM solutions may offer limited integration options, leading to compatibility issues with other enterprise systems.
- UEM: UEM solutions are designed with integration in mind. They provide robust integration capabilities, including APIs and connectors, to ensure seamless interaction with other enterprise systems.
Point 9: Automation and Self-Service
- EMM: EMM solutions automate routine tasks, such as software updates, policy enforcement, and compliance checks. They also offer self-service portals, empowering end-users to perform certain actions independently.
- MDM: MDM solutions may offer basic automation but could lack self-service capabilities.
- UEM: UEM solutions excel in automation and self-service. They streamline tasks, reduce IT workload, and enhance user satisfaction by providing advanced automation and self-service features.
Point 10: Scalability
- EMM: EMM solutions are scalable and can efficiently accommodate many devices and endpoints.
- MDM: MDM solutions may face scalability challenges, especially when managing a diverse and expanding device fleet.
- UEM: UEM solutions are inherently scalable, making them well-suited for organisations experiencing rapid growth or those seeking new technologies like IoT.
Point 11: Cloud vs. On-Premises
- EMM: EMM solutions may offer cloud and on-premises deployment options, providing flexibility to organisations based on their preferences and requirements.
- MDM: MDM solutions are often deployed on-premises, which can require substantial infrastructure investment.
- UEM: UEM solutions offer cloud-based and on-premises deployment options, allowing organisations to choose the best model with their IT strategy and infrastructure.
Point 12: Cost Considerations
- EMM: EMM solutions vary in cost, with some offering a range of pricing models, including subscription-based options. Costs depend on the chosen features and deployment model.
- MDM: MDM solutions may involve upfront licensing and ongoing maintenance expenses. The total cost of ownership (TCO) can increase as the device fleet expands.
- UEM: UEM solutions offer a range of pricing models, including subscription-based cloud solutions and free options. Organisations can select the pricing model that aligns with their device management requirements and budget constraints.
Conclusion
Making the right choice between Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM), Mobile Device Management (MDM), and Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) is crucial. Each approach offers unique advantages and limitations that can significantly impact your organisation’s security, user experience, compliance, and overall efficiency.
To explore the ideal mobile device management solution for your organisation’s unique needs, visit their website. They offer a suite of MDM solutions, including UEM and EMM, designed to address the diverse requirements of modern businesses.